HISTORY OF SMART CONTRACT
Nick Szabo, an American computer scientist who established a virtual currency called "Bit Gold" in 1998, 10 years before the development of bitcoin, introduced smart contracts in 1994. In truth, Szabo is frequently mistaken for Satoshi Nakamoto, the anonymous creator of bitcoin, a claim he has refuted. Szabo also recommended the execution of a contract for synthetic assets like derivatives and bonds in his paper. "These new securities are generated in a number of ways by mixing securities (such as bonds) and derivatives (options and futures)," Szabo stated. Due to automated analysis of these complicated term structures, very complex payment term structures may now be constructed into standardized contracts and exchanged with low transaction costs. Read More
MEANING OF SMART CONTRACT
Smart contracts are essentially programs that execute when certain criteria are satisfied and are maintained on a blockchain. They're usually used to automate the execution of an agreement so that all parties may be confident of the conclusion right away, without the need for any intermediaries or time waste. They can also automate a workflow, starting the following step when certain circumstances are satisfied. A smart contract is a self-executing contract in which the conditions of the buyer-seller agreement are put directly into lines of code.
MECHANISM OF SMART CONTRACT
Simple assertions entered into code on a blockchain are followed by smart contracts. When preset circumstances are satisfied and validated, the activities are carried out by a network of computers. These activities might include transferring payments to the proper parties, registering a vehicle, providing alerts, or issuing a ticket. When the transaction is complete, the blockchain is updated. That means the transaction can't be modified, and the results are only visible to those who have been granted access.
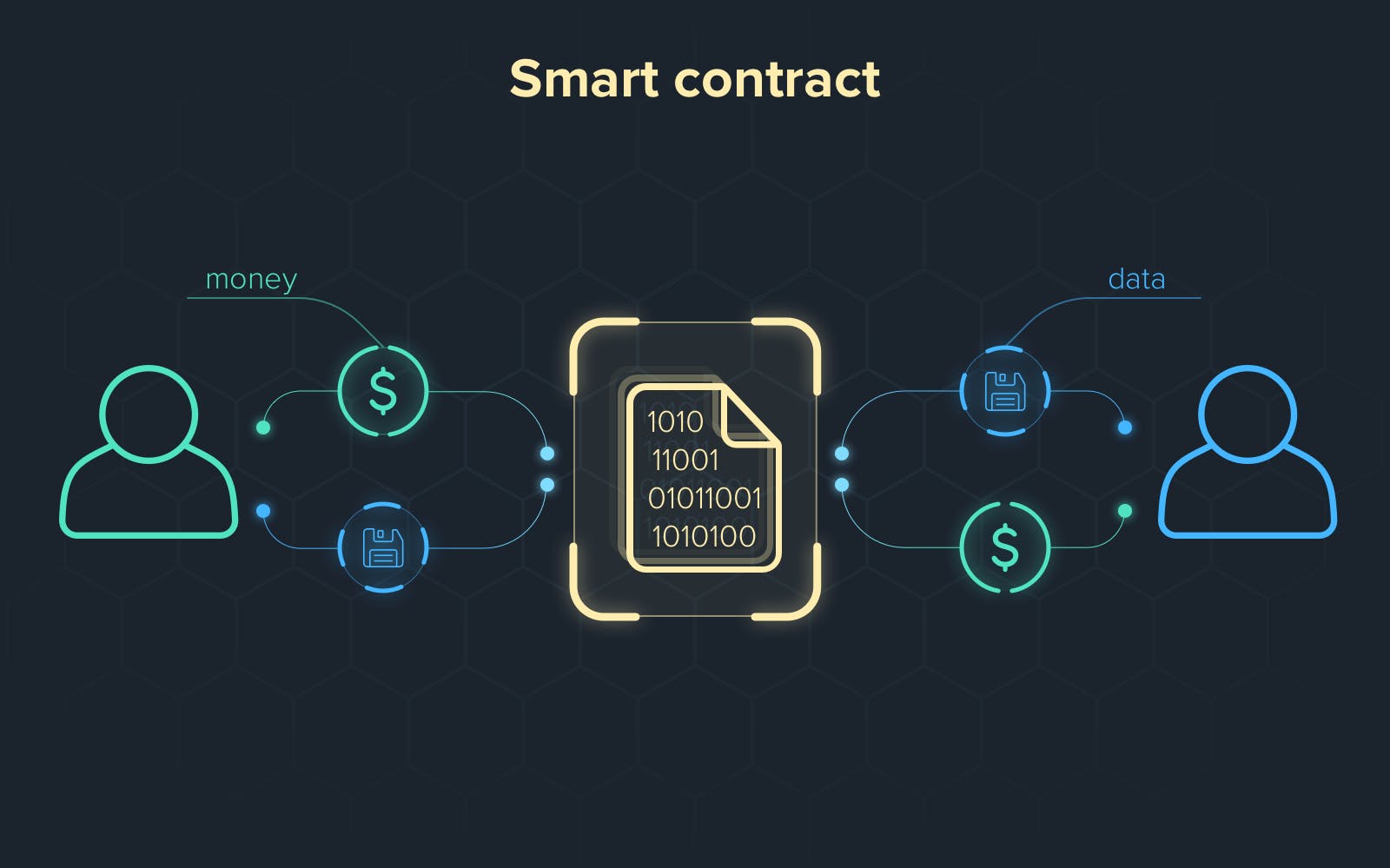
The code, as well as the agreements it contains, are disseminated throughout a decentralized blockchain network. Transactions are trackable and irreversible, and the programming regulates their execution. Smart contracts eliminate the need for a central authority, legal system, or external enforcement mechanism to carry out trustworthy transactions and agreements between distant, anonymous participants.
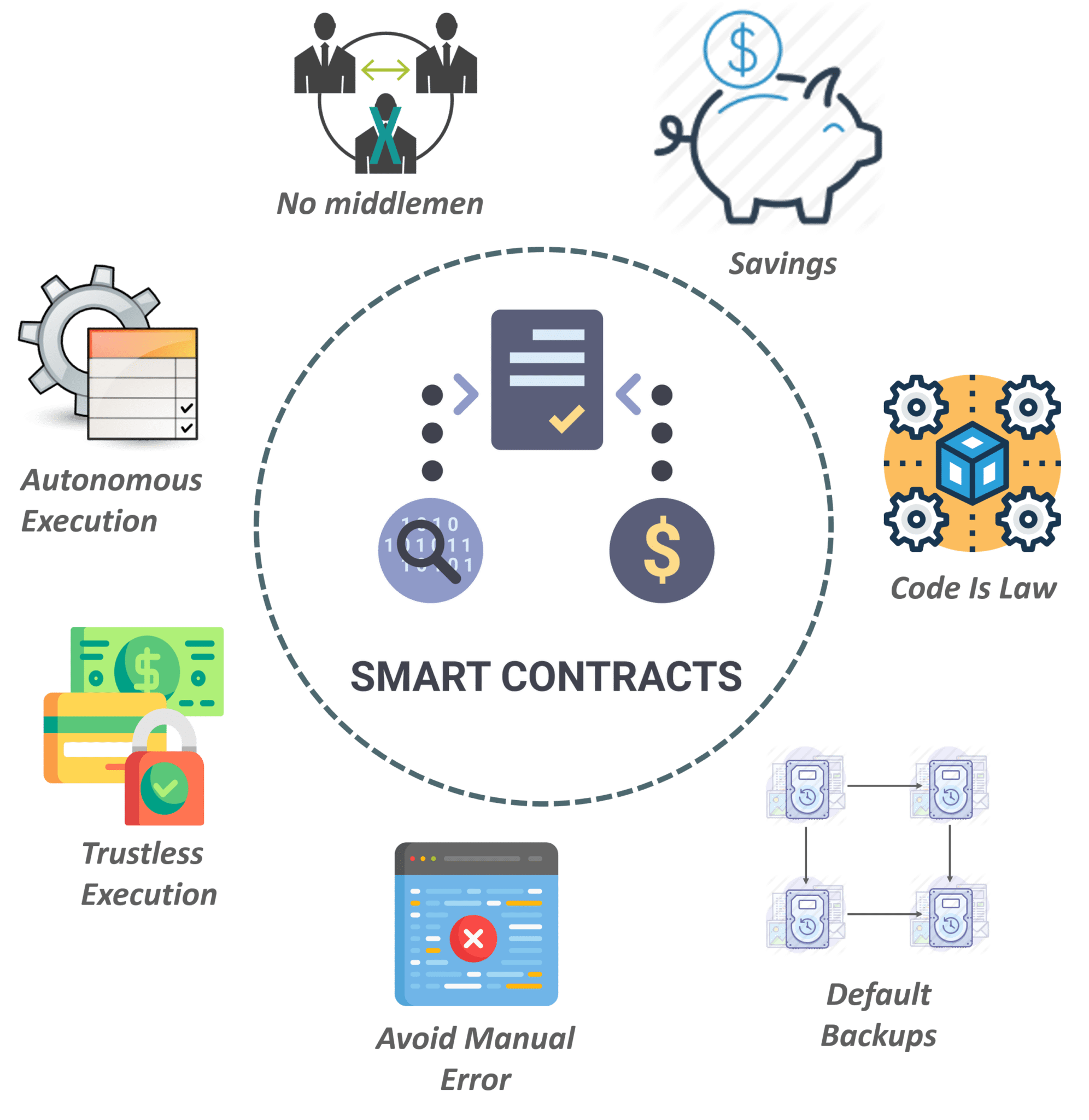
BENEFITS OF SMART CONTRACT
1. Accuracy, speed, and efficiency are all important factors.
When a condition is satisfied, the contract is instantly executed.
There is no paperwork to deal with because smart contracts are digital and automated, and no time was wasted correcting errors that often arise when filling out paperwork by hand.
2. Transparency and Trust
- Because there is no third party involved and encrypted transaction records are distributed among participants, there is no need to be concerned about information being altered with for personal advantage.
3. Savings
- Smart contracts do away with the necessity for middlemen to perform transactions, as well as the associated time delays and expenses.
4. Security
- Blockchain transaction records are particularly difficult to attack since they are encrypted. Furthermore, because each item on a distributed ledger is connected to the entries before and following it, hackers would have to alter the entire chain to modify a single record.
Conclusion
A smart contract is a business logic-encoding software that runs on a specialized virtual machine embedded in a blockchain or other distributed ledger. Read More