Table of contents
The purpose of blockchain is to enable for the recording and distribution of digital data without the ability to modify it. In this sense, a blockchain serves as the foundation for immutable ledgers, or transaction records that can't be changed, erased, or destroyed.
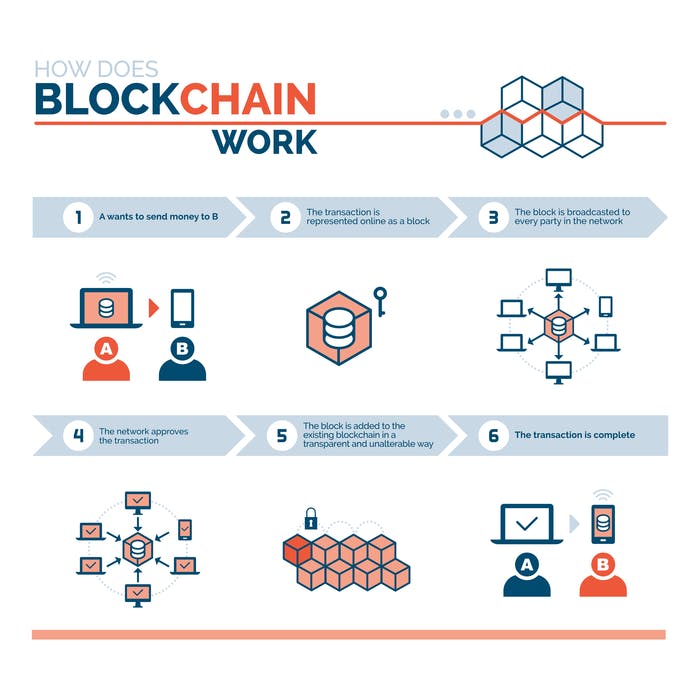
Blockchain Network
A blockchain network is a type of technological infrastructure that enables apps to connect to ledger and smart contract services. Smart contracts are generally used to create transactions, which are subsequently sent to each peer node in the network and immutably recorded on their copy of the ledger. App users include end users who use client applications and blockchain network administrators.
Types of blockchain network
A blockchain network may be created in a number of different ways.
- PUBLIC
- PRIVATE
- HYBRID
- CONSORTIUM
PUBLIC
A public blockchain is one that anybody in the world may access, submit transactions to, and expect those transactions to be included if they are genuine. It also allows anyone to participate in the consensus process, which determines which blocks are added to the chain and what the current state is. the use of cryptographic verification processes such as proof-of-work (Bitcoin) or proof-of-stake to combine economic incentives with cryptographic verification (Ethereum),keeps public blockchains safe (Ethereum). In general, these blockchains are regarded as "fully decentralized."
By establishing that specified acts are beyond the realm of even the app's creators' power, public blockchains provide a way to protect app users from their developers. Because public blockchains are open, many companies are likely to embrace them without the necessity for third-party verification.
Another reason the public blockchain has gained so many admirers is its anonymity. Yes, it is a safe and secure open platform on which you may do good and effective business. You also don't have to reveal your genuine identify or name in order to join. If your identity is protected, no one can track your network activities.
Furthermore, substantial computational power is required, transactions have little or no privacy, and security is poor. These are important issues for blockchain applications across a variety of sectors.
PRIVATE
A Private blockchain network is one that operates in a restricted context, such as a closed network, or is controlled by a single company. While it functions similarly to a public blockchain network in terms of peer-to-peer connectivity and decentralization, this blockchain is substantially smaller. Private blockchains, rather than allowing everyone to join and supply computer power, are often run on a limited network within a corporation or organization. Permissioned blockchains and business blockchains are other names for them.
Permissioned blockchains that are governed by a single entity are known as private blockchains or managed blockchains. In a private blockchain, the central authority selects who may be a node. The central authority does not necessarily provide each node the same set of permissions to perform tasks. Private blockchains, on the other hand, are only partially decentralized since public access is prohibited.
Private blockchains are appropriate for situations when the blockchain must be cryptographically secure yet the governing entity does not want the information to be viewed by the general public due to their speed.
GO TO THIS WEBSITE TO LEARN MORE
CONCLUSION
There is no central individual or organization with the capacity or ability to assert claims of control or ownership in public blockchains, such as the bitcoin blockchain. A public blockchain allows anybody to join and become a member of the consensus. It is not the fault of any single person or organization.
Private blockchains use the same technological concepts as public blockchains, but they are built and maintained by individuals or corporations. To join the network, you must have permissions. This might include a 'by invitation only' policy. The operator of a private blockchain can change the protocol or operating system.
